Overview
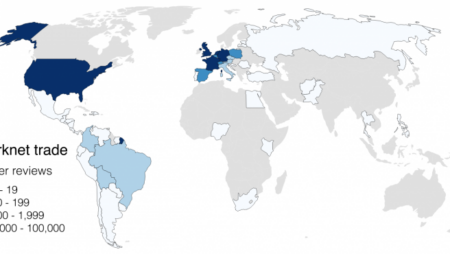
Between 2011 and 2013, the Silk Road marketplace was able to attract transactions worth hundreds of millions of dollars worth of (bitcoin-based) transactions. However, relatively little is known about the geography of this global trade. Although the strong anonymity on darknet markets prohibits any data collection about the geography of consumption, there is a large amount of data available about the sale of such goods and services.
This project thus seeks to employ techniques from computational social science and digital geography in order to achieve two primary objectives. First, we seek to scrape all relevant geographic information on darknet markets, building a re-usable data set at the country level (e.g. ‘the number of heroin sellers based in every country’, ‘the total number of vendors selling weapons in every country’ etc.). Second, we seek to map, visualize, and analyse those data: using multiple variables (the various categories of products and services) to ask ‘what is the geography of illicit products and services?’
We think this is an interesting question to ask for two reasons. First, because it connects to a wide range of societal concerns, including drug policy and public health. Observing these markets allows us to establish an evidence base to better understand a range of societal concerns, for example by tracing the global distribution of certain emergent practices. Second, it falls within our larger research interest of internet geography, where we try to understand the ways in which the internet is a localised medium, and not just a global one as is commonly assumed.
You can learn more about our upcoming work in this introductory blog post: “Exploring the Darknet in Five Easy Questions“.
Follow the project on Twitter.