
Niklas Stoehr

The Covid-19 crisis has revealed the vulnerability of the globalised economy: supply chains broke and travel restrictions made business trips nearly impossible. In particular large manufacturers have been hit hard by the crisis in the midst of a challenging long-term digital transformation process. For example, Toyota’s sales have plummeted by 45% in the first six months of 2020 and Daimler Benz has announced to lay off 15,000 employees.
At the same time, the crisis could become a facilitator of innovation as global value chains are rethought and remote working programmes are integrated into a novel organisation of work. The increased innovation pressure might help to enable change in those organisations that have struggled to adapt to 21st century business models: the world’s largest manufacturing corporations.
While agile start-ups promote digitally disrupting tools and services, the big manufacturers need to manoeuvre through a rapidly changing technological environment, despite being responsible for hundreds of thousands of employees. In this situation of rapid technological progress, it is more important than ever to gain an objective perspective on the prospects of innovations in different industries.
In our recent study Mining the Automotive Industry we aim to provide such an objective perspective of innovation and technological trends on the example of the automotive sector – one of the world’s most important industries. We apply web-mining to reveal the technological positioning of three of the world’s largest car manufacturers by only harnessing publicly-available data.
We construct large networks from the complete website structure of Volkswagen, Toyota, and Hyundai and we apply text mining to reveal the positioning of firms with regards to three innovative topics: (a) e-mobility & environment, (b) connectivity & sharing, and (c) autonomous driving & artificial intelligence.
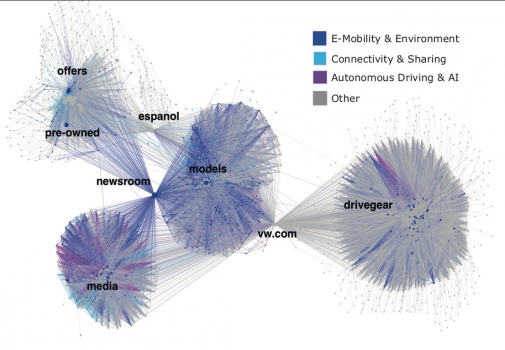
Figure 1 – Website network structure of Volkswagen (vw.com)
Our approach allows to gain insights into the innovative strategies of firms and competitive landscapes:
The resulting monitoring tool is highly transparent, reproducible and data-driven. It allows to track the positioning of innovative topics within the website networks of the three companies over time, but it can also be applied to other contexts. Thus, the methodology presented in the study can be used as a blue-print to monitor innovation and digital transformation in any industry or region.
The COVID-19 crisis led to an unprecedented economic shock. At the same time, it may also hold the chance to focus on innovation and the transformation towards 21st century business models. In fact, many of today’s most successful start-ups were founded during the Great Recession of 2008 and the recession induced substantial change in the financial sector.
Only the future will tell whether the world’s largest manufacturers catalyse the innovation pressure of the current crisis to successfully adjust their businesses to the digital transformation. The open-source tool we present here can help tracking this change process in real-time in any environment.
Read more: Stoehr N., Braesemann F., Frommelt M., Zhou S. (2020) Mining the Automotive Industry: A Network Analysis of Corporate Positioning and Technological Trends. In: Barbosa H., Gomez-Gardenes J., Gonçalves B., Mangioni G., Menezes R., Oliveira M. (eds) Complex Networks XI. Springer Proceedings in Complexity. Springer, Cham.
For reproducibility, find all code and data at: https://github.com/Braesemann/MiningAutomotiveIndustry.
